There are two main types of waves: mechanical and electromagnetic. Mechanical waves need a substance like air, water, or solids to move through, while electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space.
Mechanical waves, like sound and waves in water, move by making particles in the substance shake back and forth. Electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves, are made of electric and magnetic fields and can travel through the air.
They come in different types, like radio waves we use for phones and TV, and X-rays that help doctors see inside our bodies. Both types of waves are important in nature and in technology.
How do Mechanical Waves Move?
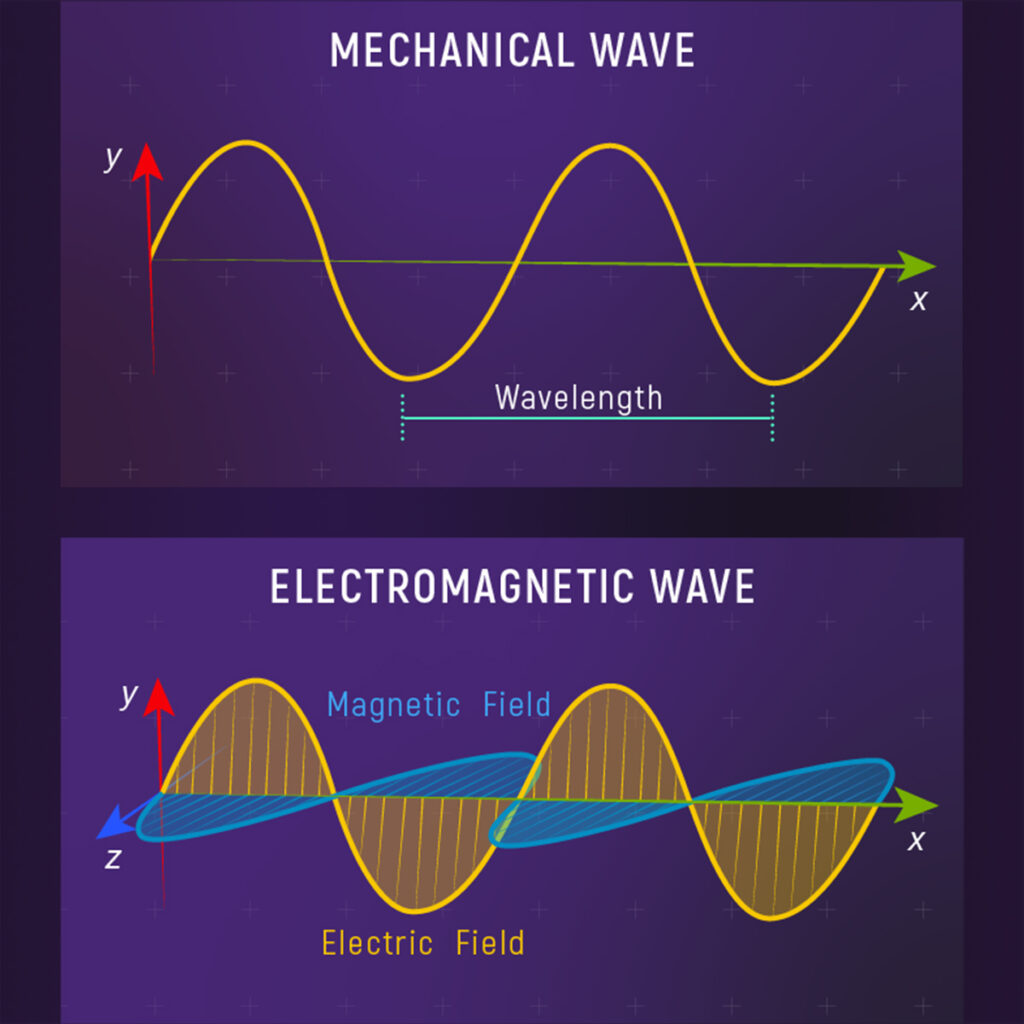
Mechanical waves, like sound waves or water waves, propagate by transferring energy through a medium. When a disturbance occurs in the medium, such as a vibration or displacement, it causes neighboring particles of the medium to also move.
These particles then transmit the disturbance to adjacent particles, and this process continues throughout the medium.
Transverse Waves
The motion of particles in transverse waves can be likened to the movement of a wave on a string. When you create a wave by shaking one end of the string, you observe a series of crests (high points) and troughs (low points) propagating along the string.
Each particle of the medium moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation. As the wave passes through, particles oscillate up and down about their equilibrium positions.
Examples of transverse waves include light waves, electromagnetic waves, and waves on a string or rope.
Longitudinal Waves
In longitudinal waves, the particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of wave propagation. Think of sound waves traveling through air.
When a sound wave passes through the air, it creates a series of compressions (regions of high pressure) and rarefactions (regions of low pressure) in the air molecules.
Each air molecule vibrates back and forth along the same direction in which the sound wave is traveling. This compression and rarefaction of air molecules transmit the sound energy from the source to the receiver.
Other examples of longitudinal waves include seismic waves (such as P-waves) traveling through the Earth and waves in springs or coils.
Surface Waves
Surface waves occur at the interface between two different media, such as water and air, or between layers of the Earth’s crust.
In water waves, for instance, the motion near the surface involves both vertical and horizontal components. Water molecules move in circular or elliptical paths, transferring energy horizontally along the surface.
Similarly, seismic surface waves combine characteristics of both longitudinal and transverse waves. They cause particles on the Earth’s surface to move both vertically and horizontally, resulting in complex motion patterns.
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
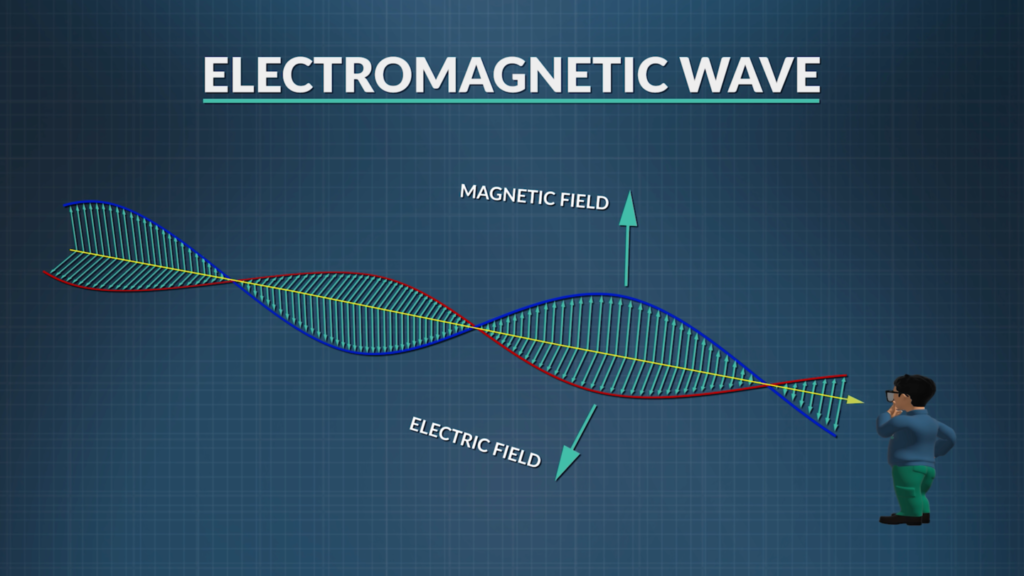
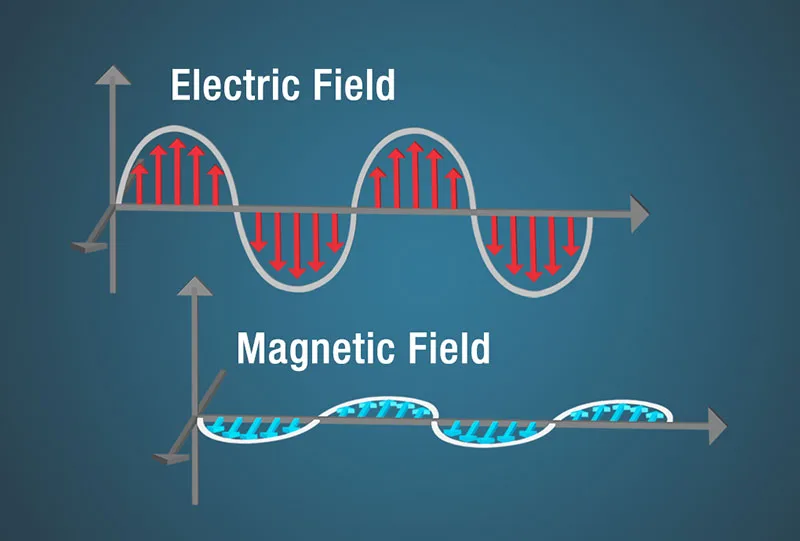
Electromagnetic waves are a type of wave that consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, propagating through space. These waves do not require a medium to travel through; they can propagate through vacuum as well as through various materials. They are produced by the acceleration of charged particles, such as electrons, and are characterized by their frequency and wavelength.
- Different Types: These waves come in lots of flavors, like radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays. Each type has its own job and properties.
- Speedy: They zip through space super fast, always moving at the same speed, which is really, really quick!
- Wiggly Motion: As they travel, electromagnetic waves wiggle side to side and up and down, like a snake slithering through the air.
- No Medium Needed: Unlike waves in water or sound waves, which need stuff to move through, like water or air, electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space just fine.
- Uses: We use these waves for lots of cool stuff, like listening to the radio, heating up food in the microwave, and even seeing inside our bodies with X-rays.
What are the Differences Between Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves?

The main differences between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves:
Medium
For them to spread, a material medium—a solid, liquid, or gas—is needed. For instance, seismic waves pass through the Earth’s crust, sound waves pass through the atmosphere, and water waves flow through water.
They can spread through a variety of materials and vacuum without the need for a medium. Without the need of any solid medium, light from the Sun travels across space to reach Earth.
Propagation
They spread by producing displacement or oscillation of the medium’s particles. The wave energy is transferred from one location to another by the motion of these particles.
Through fluctuating magnetic and electric fields, they spread. The wave travels through space as a result of interactions between these fields.
Quickness.
Mechanical Waves
The characteristics of the medium they pass through affect their speed. Sound, for instance, moves more quickly through solids than through liquids and through gasses.
In a vacuum, they move at the speed of light (c), or around 3×10^8 meters per second. Regardless of the characteristics of the medium, this speed is a basic constant of nature.
Nature
They don’t have particle-like characteristics; instead, they behave just like waves. They have characteristics of both particles and waves. In phenomena like interference and diffraction, they behave like waves, but they also behave like particles called photons, which are discrete energy packets.
FAQ’s
What is a mechanical wave?
A mechanical wave is a type of wave that needs something, like water or air, to move through. It makes things shake as it travels.
What are the 7 electromagnetic waves?
There are seven types of electromagnetic waves: radio waves (for radios), microwaves (for heating food), infrared (for remote controls), visible light (what we see), ultraviolet (from the Sun), X-rays (for seeing inside bodies), and gamma rays (from outer space).
Which wave is called a mechanical wave?
A mechanical wave is called a wave that needs a material, like water or air, to travel. Examples include waves in water and sound waves in the air.
What do you mean by electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are special kinds of waves that travel through space without needing anything to move through. They include things like light and radio waves.
What is a mechanical wave definition for kids?
A mechanical wave is like a ripple in water or a sound traveling through the air. It needs something to move through, unlike light which can travel through space without anything there.
Final Words
So, that’s the end of our talk about waves! We learned about two kinds: ones that need stuff to move through, like sound and water waves, and ones that can travel through the air, like light and radio waves.
They’re important for nature and technology, so it’s cool to know about them! Waves are everywhere, and knowing about them helps us understand things better!